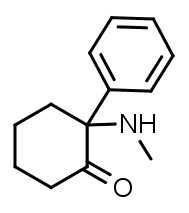
Deschloroketamine (DCK) is a dissociative drug that has recently gained popularity. It’s a derivative of ketamine, a popular anesthetic drug known for its dissociative effects. DCK is a more potent and longer-lasting alternative to ketamine, and it’s been reported to produce effects like dissociation, euphoria, and hallucinations. This article will provide an overview of DCK, including its general information, history, dosage, administration, user reviews, and more.
General Information on Deschloroketamine
The DCK research chemical is a white crystalline powder that’s soluble in water and alcohol. It’s different from ketamine in that it has a chlorine atom removed from the phenyl ring (a group of atoms). DCK is classified as a dissociative drug, producing a sense of detachment from reality. This feeling results in dissociation, depersonalization, and derealization. It’s also known to cause feelings of euphoria, hallucinations, and cognitive impairment.
DCK is usually sold as a powder or crystal, and it can be administered through various routes. Such routes include oral administration, nasal insufflation, vaporization, and suppository, which we’ll cover later on. The effects of DCK can last for several hours, and they are known to be more potent and longer-lasting than ketamine. Users looking for legal highs may need to find an alternative, as this drug is illegal in many countries. However, it could be in a gray legal area, so it might technically rank with legal drugs depending on location.
History of Deschloroketamine
Next in this research chemical review, we’ll cover the history of this drug. DCK’s history dates back to the 1960s when Parke-Davis first created it. However, it was never marketed for medical use. In fact, its potential as a recreational drug was not explored until much later. In the 2010s, DCK started to gain popularity in the underground drug market. Since then, it’s become a popular alternative to ketamine.
Using DCK has caused several reported adverse effects, including psychosis, seizures, and fatalities. Despite these risks, DCK continues to be used by many people for its dissociative effects.
Dosage and Administration
Now, we’ll examine the dosage and administration as part of this DCK review. There are many routes through which users can administer this drug. Those include oral administration, nasal insufflation, vaporization, and suppository. The appropriate dosage of DCK depends on several factors, including the user’s body weight, tolerance, and route of administration.
Oral Administration
When administered orally, DCK is usually mixed with a liquid, like water or juice. Then, the user simply swallows the mixture. The onset of effects can take 20 minutes to 2 hours, depending on metabolism and the food volume in the user’s stomach. The effects of oral administration are known to be less intense than other routes of administration, but they can last for several hours.
Nasal Insufflation
This is another popular route of administration for DCK. The powder or crystal is snorted through the nostrils. Users can feel the effects within minutes. Nasal insufflation produces a more intense and shorter-lasting high than oral administration.
Vaporization
Vaporization is a relatively new route of administration for DCK that involves heating the powder or crystal to produce a vapor that is inhaled. Vaporization produces a quick onset of effects and a more intense high than oral administration.
Suppository
A suppository is certainly a less common route of administration for DCK. This unique administration method involves injecting the drug into the rectum using a suppository. The effects are similar to those of oral administration but could be even more intense.
Redosing
Redosing is when users take additional doses of DCK after the initial dose wears off. It’s possible with DCK but can lead to an increase in the drug’s side effects. Users should wait at least 2 hours after their initial dose before redosing.
User Deschloroketamine Reviews
User reviews of DCK vary widely, with some users reporting positive experiences and others reporting negative experiences. Some users report feeling relaxed and euphoric after taking DCK, while others report feeling anxious and paranoid. The drug’s effects also vary based on the dosage and method of administration. So, there’s no reliable way to predict which effect a new user will experience and to what degree.
Onset of Effects
In general, the onset of effects for DCK typically occurs within 10-20 minutes of use, although this can vary among individuals and depending on factors such as dosage, purity, and method of administration. The effects of DCK can last for several hours, with some users reporting residual effects for up to 24 hours after use.
Dissociation
Users of DCK report experiencing a range of dissociative effects. They include a sense of detachment or disconnection from reality, altered perception of time and space, and changes in sensory experiences like sight, sound, and touch.
Some users report experiencing a sense of euphoria or calmness, while others may experience confusion, disorientation, or anxiety. The dissociative effects of this research chemical can vary widely among individuals and depend on factors such as dosage, purity, and method of administration.
Altered Perception of Time
This effect can manifest in a variety of ways. Users report feelings of time slowing down or speeding up. They may also feel a sense of timelessness or detachment from the present moment.
Some users may feel like everyday activities are more drawn out than usual. Others may experience a sense of time dilation, where time seems to move faster. Additionally, some users may feel like they’re outside of time or that time no longer exists.
The altered perception of time can be disorienting or confusing for some users. It might even contribute to other psychological effects such as anxiety, confusion, or a distorted sense of reality.
Hallucinations
Users of DCK and other dissociative substances report experiencing visual and auditory hallucinations. For some people, the hallucinogenic effects of DCK may be enjoyable or therapeutic. However, for others, they may be unsettling or uncomfortable.
Anticlimax (“Comedown”)
Some users have reported experiencing a range of after-effects following DCK use, including physical symptoms such as fatigue, headache, and nausea, as well as psychological symptoms such as anxiety, depression, and difficulty concentrating. These effects may be more pronounced following higher doses or prolonged substance use.
Potential Side Effects of Deschloroketamine
Potential side effects of DCK use can include nausea, vomiting, dizziness, confusion, and disorientation. In addition, high doses or prolonged use can also increase the risk of more severe side effects such as seizures, respiratory depression, and even death. Long-term use of dissociative substances like DCK can also lead to psychological and cognitive problems like memory loss, anxiety, depression, and psychosis.
It is important to note that the use of DCK and other research chemicals is not approved for human consumption and is not subject to regulation by health authorities. Therefore, the purity and safety of these substances cannot be guaranteed, and users are taking significant risks by consuming them.
The information provided in Express Highs Blog is intended for educational, informational, and harm-reduction purposes only. The content published on this page does not encourage, promote, or condone the use, purchase, sale, or distribution of any controlled or psychoactive substances.
Many compounds discussed on this website may be regulated or prohibited in certain countries or jurisdictions. Laws and regulations change frequently, and it is the responsibility of each reader to understand and comply with the local laws applicable in their location before engaging with any substance mentioned.
Articles published in this category may reference scientific research, anecdotal experiences, historical context, or emerging trends. However, the content should not be interpreted as medical advice, legal advice, or professional guidance of any kind. Always consult a qualified medical professional before making decisions that could impact your physical or mental health.